Java多線程之深入理解ReentrantLock
保證線程安全的方式有很多,比如CAS操作、synchronized、原子類、volatile保證可見性和ReentrantLock等,這篇文章我們主要探討ReentrantLock的相關(guān)內(nèi)容。本文基于JDK1.8講述ReentrantLock.
一、可重入鎖所謂可重入鎖,即一個(gè)線程已經(jīng)獲得了某個(gè)鎖,當(dāng)這個(gè)線程要再次獲取這個(gè)鎖時(shí),依然可以獲取成功,不會(huì)發(fā)生死鎖的情況。synchronized就是一個(gè)可重入鎖,除此之外,JDK提供的ReentrantLock也是一種可重入鎖。
二、ReentrantLock2.1 ReentrantLock的簡(jiǎn)單使用public class TestReentrantLock {private static int i = 0;public static void main(String[] args) {ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock();try { lock.lock(); i++;} finally { lock.unlock();}System.out.println(i);}}
上面是ReentrantLock的一個(gè)簡(jiǎn)單使用案列,進(jìn)入同步代碼塊之前,需要調(diào)用lock()方法進(jìn)行加鎖,執(zhí)行完同步代碼塊之后,為了防止異常發(fā)生時(shí)造成死鎖,需要在finally塊中調(diào)用unlock()方法進(jìn)行解鎖。
2.2 ReentrantLock UML圖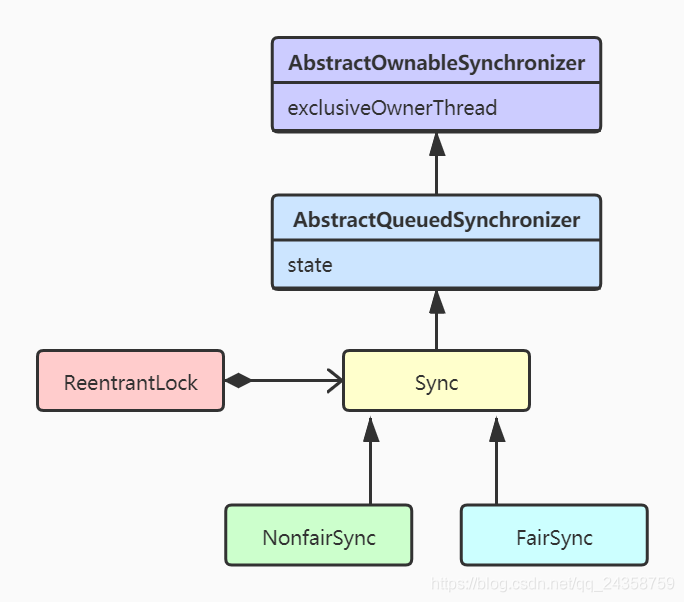
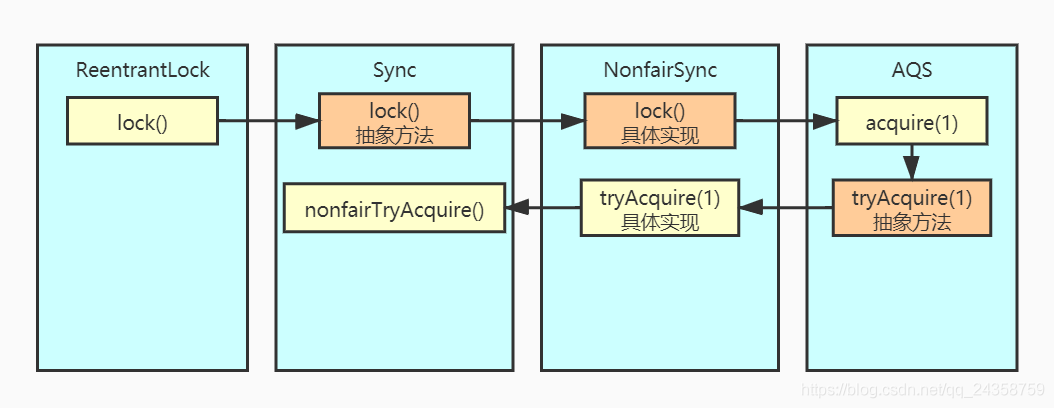
上圖描述了ReentrantLock.lock()加鎖的方法調(diào)用過程。在ReentrantLock中有一個(gè)成員變量private final Sync sync,Sync是AQS的一個(gè)子類。ReentrantLock的lock()方法中,調(diào)用了sync的lock()方法,這個(gè)方法為抽象方法,具體調(diào)用的是NonfairSync中實(shí)現(xiàn)的lock()方法:
/** * Performs lock. Try immediate barge, backing up to normal * acquire on failure. */final void lock() { if (compareAndSetState(0, 1))setExclusiveOwnerThread(Thread.currentThread()); elseacquire(1);}
在這個(gè)方法中,先嘗試通過CAS操作進(jìn)行加鎖。如果加鎖失敗,會(huì)調(diào)用AQS的acquire()方法:
/** * Acquires in exclusive mode, ignoring interrupts. Implemented * by invoking at least once {@link #tryAcquire}, * returning on success. Otherwise the thread is queued, possibly * repeatedly blocking and unblocking, invoking {@link * #tryAcquire} until success. This method can be used * to implement method {@link Lock#lock}. * * @param arg the acquire argument. This value is conveyed to *{@link #tryAcquire} but is otherwise uninterpreted and *can represent anything you like. */public final void acquire(int arg) { if (!tryAcquire(arg) &&acquireQueued(addWaiter(Node.EXCLUSIVE), arg))selfInterrupt();}
在AQS的acquire方法中,先嘗試調(diào)用tryAcquire方法進(jìn)行加鎖,如果失敗,會(huì)調(diào)用acquireQueued進(jìn)入等待隊(duì)列當(dāng)中。acquireQueued方法將會(huì)在第三章中講解,先來看tryAcquire方法的內(nèi)容。AQS的tryAcquire方法是一個(gè)模板方法,其具體實(shí)現(xiàn)在NonfairSync的tryAcquire方法中,里面僅僅是調(diào)用了nonfairTryAcquire方法:
/** * Performs non-fair tryLock. tryAcquire is implemented in * subclasses, but both need nonfair try for trylock method. */final boolean nonfairTryAcquire(int acquires) { final Thread current = Thread.currentThread(); int c = getState(); if (c == 0) {if (compareAndSetState(0, acquires)) { setExclusiveOwnerThread(current); return true;} } else if (current == getExclusiveOwnerThread()) {int nextc = c + acquires;if (nextc < 0) // overflow throw new Error('Maximum lock count exceeded');setState(nextc);return true; } return false;}
在這個(gè)方法中,先獲取state判斷其是否為0。如果為0表示沒有其他線程占用鎖,會(huì)嘗試通過CAS操作將state設(shè)為1進(jìn)行加鎖;如果state不為0,表示某個(gè)線程已經(jīng)占用了鎖,判斷占用鎖的線程是否為當(dāng)前線程,如果是,則將state進(jìn)行加1的操作,這就是ReentrantLock可重入的實(shí)現(xiàn)原理。
三、AQSAQS即AbstractQueuedSynchronizer。AQS提供了一個(gè)基于FIFO隊(duì)列,可以用于構(gòu)建鎖或者其他相關(guān)同步裝置的基礎(chǔ)框架。AQS其實(shí)是CLH(Craig,Landin,Hagersten)鎖的一個(gè)變種,下面來講解AQS的核心思想及其具體實(shí)現(xiàn)。
3.1 state/** * The synchronization state. */ private volatile int state;
state是AQS中最核心的成員變量。這是一個(gè)volatile變量,當(dāng)其為0時(shí),表示沒有任何線程占用鎖。線程通過CAS將state從0置為1進(jìn)行加鎖,當(dāng)線程持有鎖的情況下,再次進(jìn)行加鎖,會(huì)將state加1,即重入。
3.2 exclusiveOwnerThread/** * The current owner of exclusive mode synchronization. */ private transient Thread exclusiveOwnerThread;
exclusiveOwnerThread是AQS的父類AbstractOwnableSynchronizer中的成員變量,其作用是實(shí)現(xiàn)可重入機(jī)制時(shí),用于判斷持有鎖的線程是否為當(dāng)前線程。
3.3 AQS等待隊(duì)列除了以上state和exclusiveOwnerThread兩個(gè)重要的成員變量以外,AQS還維護(hù)了一個(gè)等待隊(duì)列。當(dāng)線程嘗試加鎖失敗時(shí),會(huì)進(jìn)入這個(gè)等待隊(duì)列中,這也是整個(gè)AQS中最核心的內(nèi)容。這個(gè)等待隊(duì)列是一個(gè)雙向鏈表,其節(jié)點(diǎn)Node對(duì)等待加鎖的線程進(jìn)行封裝。

/** * Creates and enqueues node for current thread and given mode. * * @param mode Node.EXCLUSIVE for exclusive, Node.SHARED for shared * @return the new node */private Node addWaiter(Node mode) { Node node = new Node(Thread.currentThread(), mode); // Try the fast path of enq; backup to full enq on failure Node pred = tail; if (pred != null) {node.prev = pred;// 通過CAS操作將自身追加到鏈表尾部if (compareAndSetTail(pred, node)) { pred.next = node; return node;} } enq(node); return node;}
當(dāng)線程嘗試加鎖失敗時(shí),通過CAS操作將自身追加到鏈表尾部。入隊(duì)之后,會(huì)調(diào)用acquireQueued在隊(duì)列中嘗試加鎖:
/** * Acquires in exclusive uninterruptible mode for thread already in * queue. Used by condition wait methods as well as acquire. * * @param node the node * @param arg the acquire argument * @return {@code true} if interrupted while waiting */ final boolean acquireQueued(final Node node, int arg) {boolean failed = true;try { boolean interrupted = false; for (;;) {final Node p = node.predecessor();if (p == head && tryAcquire(arg)) { setHead(node); p.next = null; // help GC failed = false; return interrupted;}if (shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(p, node) && parkAndCheckInterrupt()) interrupted = true; }} finally { if (failed)cancelAcquire(node);} }
在這個(gè)方法中,會(huì)判斷其前置節(jié)點(diǎn)是否為頭節(jié)點(diǎn),如果是,則嘗試進(jìn)行加鎖。如果加鎖失敗,則調(diào)用LockSupport.park方法進(jìn)入阻塞狀態(tài),等待其前置節(jié)點(diǎn)釋放鎖之后將其喚醒。
3.4 AQS中的模板方法設(shè)計(jì)模式AQS完美地運(yùn)用了模板方法設(shè)計(jì)模式,其中定義了一系列的模板方法。比如以下方法:
// 互斥模式下使用:嘗試獲取鎖protected boolean tryAcquire(int arg) {throw new UnsupportedOperationException();}// 互斥模式下使用:嘗試釋放鎖protected boolean tryRelease(int arg) {throw new UnsupportedOperationException();}// 共享模式下使用:嘗試獲取鎖protected int tryAcquireShared(int arg) {throw new UnsupportedOperationException();}// 共享模式下使用:嘗試釋放鎖protected boolean tryReleaseShared(int arg) {throw new UnsupportedOperationException();}
這些方法在AQS中只拋出了UnsupportedOperationException異常,所以需要子類去實(shí)現(xiàn)它們。之所以沒有將這些方法設(shè)計(jì)成為抽象方法,是因?yàn)锳QS的子類可能只需要實(shí)現(xiàn)其中的某些方法即可實(shí)現(xiàn)其功能。
總結(jié)不同版本的JDK,AQS的實(shí)現(xiàn)可能會(huì)有細(xì)微的差異,但其核心思想是不會(huì)變的,即線程加鎖失敗后,通過CAS進(jìn)行入隊(duì)的操作,并通過CAS的方法設(shè)置state來獲得鎖。
到此這篇關(guān)于Java多線程之深入理解ReentrantLock的文章就介紹到這了,更多相關(guān)Java ReentrantLock總結(jié)內(nèi)容請(qǐng)搜索好吧啦網(wǎng)以前的文章或繼續(xù)瀏覽下面的相關(guān)文章希望大家以后多多支持好吧啦網(wǎng)!
相關(guān)文章:
1. 利用CSS制作3D動(dòng)畫2. 讀大數(shù)據(jù)量的XML文件的讀取問題3. 存儲(chǔ)于xml中需要的HTML轉(zhuǎn)義代碼4. 使用Spry輕松將XML數(shù)據(jù)顯示到HTML頁的方法5. html5手機(jī)觸屏touch事件介紹6. 用xslt+css讓RSS顯示的跟網(wǎng)頁一樣漂亮7. 《CSS3實(shí)戰(zhàn)》筆記--漸變?cè)O(shè)計(jì)(一)8. 測(cè)試模式 - XSL教程 - 59. CSS3實(shí)現(xiàn)動(dòng)態(tài)翻牌效果 仿百度貼吧3D翻牌一次動(dòng)畫特效10. HTML5 Canvas繪制圖形從入門到精通
 網(wǎng)公網(wǎng)安備
網(wǎng)公網(wǎng)安備