Python 數據科學 Matplotlib圖庫詳解
Matplotlib 是 Python 的二維繪圖庫,用于生成符合出版質量或跨平臺交互環境的各類圖形。
圖形解析與工作流圖形解析

工作流
Matplotlib 繪圖的基本步驟:1 準備數據
2 創建圖形
3 繪圖
4 自定義設置
5 保存圖形
6 顯示圖形
import matplotlib.pyplot as pltx = [1,2,3,4] # step1y = [10,20,25,30]fig = plt.figure() # step2ax = fig.add_subplot(111) # step3ax.plot(x, y, color=’lightblue’, linewidth=3) # step34ax.scatter([2,4,6], [5,15,25], color=’darkgreen’, marker=’^’)ax.set_xlim(1, 6.5)plt.savefig(’foo.png’) # step5plt.show() # step6
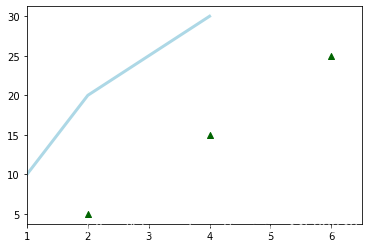
一維數據
import numpy as np x = np.linspace(0, 10, 100)y = np.cos(x) z = np.sin(x)
二維數據或圖片
data = 2 * np.random.random((10, 10))data2 = 3 * np.random.random((10, 10))Y, X = np.mgrid[-3:3:100j, -3:3:100j]U = -1 - X**2 + YV = 1 + X - Y**2from matplotlib.cbook import get_sample_dataimg = np.load(’E:/anaconda3/envs/torch/Lib/site-packages/matplotlib/mpl-data/aapl.npz’)
繪制圖形
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
畫布
fig = plt.figure()fig2 = plt.figure(figsize=plt.figaspect(2.0))
坐標軸
圖形是以坐標軸為核心繪制的,大多數情況下,子圖就可以滿足需求。子圖是柵格系統的坐標軸。
fig.add_axes()ax1 = fig.add_subplot(221) # row-col-numax3 = fig.add_subplot(212) fig3, axes = plt.subplots(nrows=2,ncols=2)fig4, axes2 = plt.subplots(ncols=3)

一維數據
fig, ax = plt.subplots()lines = ax.plot(x,y) # 用線或標記連接點ax.scatter(x,y) # 縮放或著色未連接的點axes[0,0].bar([1,2,3],[3,4,5]) # 繪制等寬縱向矩形axes[1,0].barh([0.5,1,2.5],[0,1,2]) # 繪制等高橫向矩形axes[1,1].axhline(0.45) # 繪制與軸平行的橫線axes[0,1].axvline(0.65) # 繪制與軸垂直的豎線ax.fill(x,y,color=’blue’) # 繪制填充多邊形ax.fill_between(x,y,color=’yellow’) # 填充y值和0之間
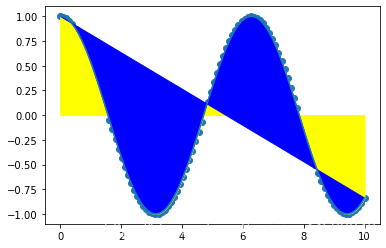
二維數據或圖片
import matplotlib.image as imgpltimg = imgplt.imread(’C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/timg.jpg’) fig, ax = plt.subplots()im = ax.imshow(img, cmap=’gist_earth’, interpolation=’nearest’, vmin=-200, vmax=200)# 色彩表或RGB數組 axes2[0].pcolor(data2) # 二維數組偽彩色圖axes2[0].pcolormesh(data) # 二維數組等高線偽彩色圖CS = plt.contour(Y,X,U) # 等高線圖axes2[2].contourf(data) axes2[2]= ax.clabel(CS) # 等高線圖標簽

向量場
axes[0,1].arrow(0,0,0.5,0.5) # 為坐標軸添加箭頭axes[1,1].quiver(y,z) # 二維箭頭axes[0,1].streamplot(X,Y,U,V) # 二維箭頭
數據分布
ax1.hist(y) # 直方圖ax3.boxplot(y) # 箱形圖ax3.violinplot(z) # 小提琴圖
自定義圖形 顏色、色條與色彩表
plt.plot(x, x, x, x**2, x, x**3)ax.plot(x, y, alpha = 0.4)ax.plot(x, y, c=’k’)fig.colorbar(im, orientation=’horizontal’)im = ax.imshow(img, cmap=’seismic’)
標記
fig, ax = plt.subplots()ax.scatter(x,y,marker='.')ax.plot(x,y,marker='o')

線型
plt.plot(x,y,linewidth=4.0)plt.plot(x,y,ls=’solid’) plt.plot(x,y,ls=’--’)plt.plot(x,y,’--’,x**2,y**2,’-.’)plt.setp(lines,color=’r’,linewidth=4.0)
文本與標注
ax.text(1, -2.1,’Example Graph’,style=’italic’)ax.annotate('Sine', xy=(8, 0), xycoords=’data’, xytext=(10.5, 0), textcoords=’data’, arrowprops=dict(arrowstyle='->', connectionstyle='arc3'),)
數學符號
plt.title(r’$sigma_i=15$’, fontsize=20)尺寸限制、圖例和布局
尺寸限制與自動調整
ax.margins(x=0.0,y=0.1) # 添加內邊距ax.axis(’equal’) # 將圖形縱橫比設置為1ax.set(xlim=[0,10.5],ylim=[-1.5,1.5]) # 設置x軸與y軸的限ax.set_xlim(0,10.5)
圖例
ax.set(title=’An Example Axes’, ylabel=’Y-Axis’, xlabel=’X-Axis’) # 設置標題與x、y軸的標簽ax.legend(loc=’best’) # 自動選擇最佳的圖例位置
標記
ax.xaxis.set(ticks=range(1,5), ticklabels=[3,100,-12,'foo']) # 手動設置X軸刻度ax.tick_params(axis=’y’, direction=’inout’, length=10) # 設置Y軸長度與方向
子圖間距
fig3.subplots_adjust(wspace=0.5, hspace=0.3, left=0.125, right=0.9, top=0.9, bottom=0.1)fig.tight_layout() # 設置畫布的子圖布局
坐標軸邊線
ax1.spines[’top’].set_visible(False) # 隱藏頂部坐標軸線ax1.spines[’bottom’].set_position((’outward’,10)) # 設置底部邊線的位置為outward
保存
#保存畫布plt.savefig(’foo.png’)# 保存透明畫布plt.savefig(’foo.png’, transparent=True)
顯示圖形
plt.show()
關閉與清除
plt.cla() # 清除坐標軸plt.clf() # 清除畫布plt.close() # 關閉窗口
以上就是Python 數據科學 Matplotlib的詳細內容,更多關于Python 數據科學 Matplotlib的資料請關注好吧啦網其它相關文章!
相關文章:
 網公網安備
網公網安備