Python網絡編程之ZeroMQ知識總結
總結以下:ØMQ (ZeroMQ) 是一個基于消息隊列的多線程網絡庫,它封裝了網絡通信、消息隊列、線程調度等功能,向上層提供簡潔的API,應用程序通過加載庫文件,調用API函數來實現高性能網絡通信。
看起來有些抽象,下面我們結合ZeroMQ 的 Python 封裝———— pyzmp,用實例看一下ZeroMQ的三種最基本的工作模式。
二、安裝安裝方法
pip install pyzmq
查看是否安裝成功
>>> import zmq>>> print(zmq.__version__)22.0.3三、Request-Reply (請求響應模式)3.1 Request-Reply模式概述: 消息雙向的,有來有往。 Client請求的消息,Server必須答復給Client。 Client在請求后,Server必須回響應,注意:Server不返回響應會報錯。 Server和Client都可以是1:N的模型。通常把1認為是Server,N認為是Client。 更底層的端點地址是對上層隱藏的,每個請求都隱含回應地址,而應用則不關心它。 ZMQ 可以很好的支持路由功能(實現路由功能的組件叫做 Device),把 1:N 擴展為 N:M(只需要加入若干路由節點)。
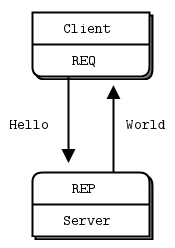
#client.pyimport zmqcontext = zmq.Context()# Socket to talk to serverprint('Connecting to hello world server…')socket = context.socket(zmq.REQ)socket.connect('tcp://localhost:5555')socket.send(b'Hello')# Get the reply.message = socket.recv()print(f'Received reply [ {message} ]')3.3 Server端python實現
#server.pyimport timeimport zmqcontext = zmq.Context()socket = context.socket(zmq.REP)socket.bind('tcp://*:5555')while True: # Wait for next request from client message = socket.recv() print('Received request: %s' % message) # Do some ’work’ time.sleep(1) # Send reply back to client socket.send(b'World') 啟動client.py 首先會打印Connecting to hello world server… 但不會受到任何消息。 然后啟動server.py ,客戶端收到來自客戶端的request: b’Hello’ 此時client端收到來自server端的 reply: [ b’World’ ]
python client.py Connecting to hello world server…Received reply [ b’World’ ]
python server.py Received request: b’Hello’
可以試一下,多運行幾個client.py,看看情況是什么樣的。

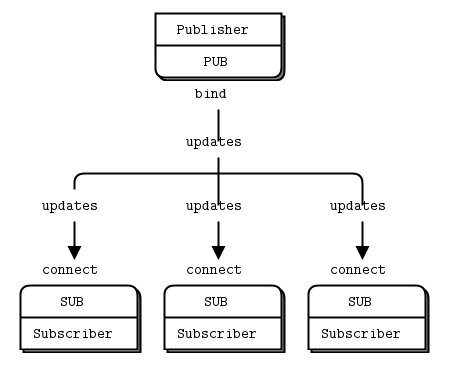
這里直接引用官方文檔的例子:
發布者:類似于一個天氣更新服務器,向訂閱者發送天氣更新,內容包括郵政編碼、溫度、濕度等信息
#Publisher.pyimport zmqfrom random import randrangecontext = zmq.Context()socket = context.socket(zmq.PUB)socket.bind('tcp://*:5556')while True: zipcode = randrange(1, 100000) temperature = randrange(-80, 135) relhumidity = randrange(10, 60) socket.send_string('%i %i %i' % (zipcode, temperature, relhumidity))
訂閱者:它監聽發布者更新的數據流,過濾只接收與特定郵政編碼相關的天氣信息,默認接收接收10條數據
#Subscribe.py import sysimport zmq# Socket to talk to servercontext = zmq.Context()socket = context.socket(zmq.SUB)print('Collecting updates from weather server...')socket.connect('tcp://localhost:5556')# Subscribe to zipcode, default is NYC, 10001zip_filter = sys.argv[1] if len(sys.argv) > 1 else '10001'# Python 2 - ascii bytes to unicode strif isinstance(zip_filter, bytes): zip_filter = zip_filter.decode(’ascii’)socket.setsockopt_string(zmq.SUBSCRIBE, zip_filter)# Process 5 updatestotal_temp = 0for update_nbr in range(5): string = socket.recv_string() zipcode, temperature, relhumidity = string.split() total_temp += int(temperature)print( 'Average temperature for zipcode ’%s’ was %dF' % (zip_filter, total_temp / (update_nbr + 1)))

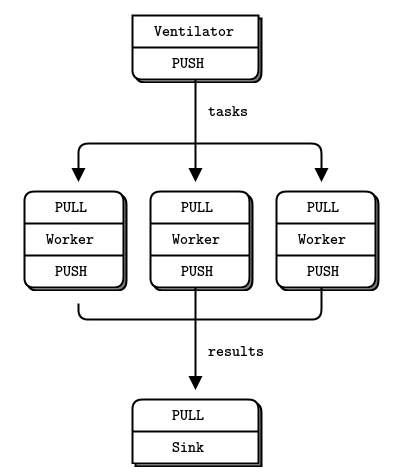
ventilator 使用的是 SOCKET_PUSH,將任務分發到 Worker 節點上。Worker 節點上,使用 SOCKET_PULL 從上游接受任務,并使用 SOCKET_PUSH 將結果匯集到 Sink。值得注意的是,任務的分發的時候也同樣有一個負載均衡的路由功能,worker 可以隨時自由加入,ventilator 可以均衡將任務分發出去。
Push/Pull模式還是蠻常用的,這里我們主要測試一下它的負載均衡。
5.2 Ventilator# ventilator.pyimport zmqimport timecontext = zmq.Context()socket = context.socket(zmq.PUSH)socket.bind('tcp://*:5557')while True: socket.send(b'test') print('已發送') time.sleep(1)5.3 worker
# worker.pyimport zmqcontext = zmq.Context()recive = context.socket(zmq.PULL)recive.connect(’tcp://127.0.0.1:5557’)sender = context.socket(zmq.PUSH)sender.connect(’tcp://127.0.0.1:5558’)while True: data = recive.recv() print('work1 正在轉發...') sender.send(data)5.4 sink
# sink.pyimport zmqimport syscontext = zmq.Context()socket = context.socket(zmq.PULL)socket.bind('tcp://*:5558')while True: response = socket.recv() print('response: %s' % response)
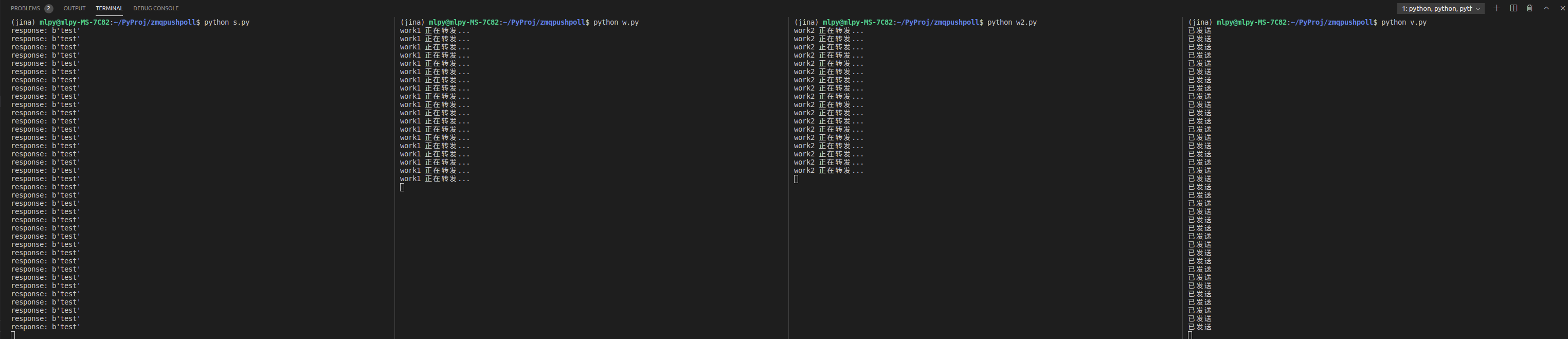
打開4個Terminal,分別運行
python sink.pypython worker.pypython worker.pypython ventilator.py
消息模型可以根據需要組合使用,后續的代理模式和路由模式等都是在三種基本模式上面的擴展或變異。
到此這篇關于Python網絡編程之ZeroMQ知識總結的文章就介紹到這了,更多相關Python ZeroMQ知識總結內容請搜索好吧啦網以前的文章或繼續瀏覽下面的相關文章希望大家以后多多支持好吧啦網!
相關文章:

 網公網安備
網公網安備